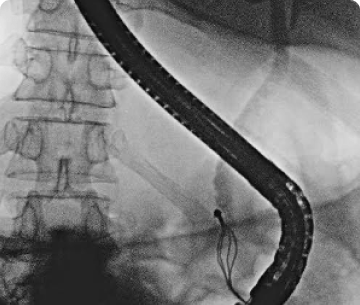
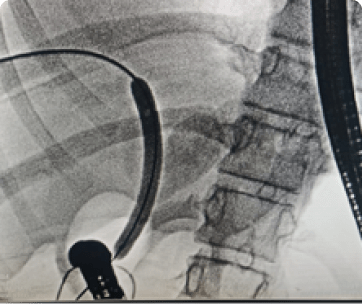
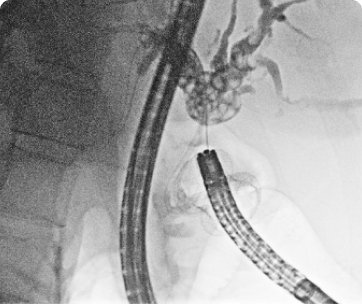
ESOPHAGEAL MANOMETRY
An esophageal manometry is a medical device used to measure pressure and movement in the esophagus, the muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach.
ESOPHAGEAL MANOMETRY

An esophageal manometry is a medical device used to measure pressure and movement in the esophagus, the muscular tube that connects the throat to the stomach.
Esophageal manometry is performed to evaluate the function of the esophagus and diagnose conditions such as achalasia, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and other motility disorders.
1,11,1000+ CASES HANDLED
3 HI-TECH ENDOSCOPY DEVICES
5+ SPECIALIST GI ENDOSCOPIST
Esophageal manometry is performed by passing a thin, flexible tube through the nose and into the esophagus. The tube contains pressure sensors that measure the muscle contractions and relaxation in the esophagus.
Esophageal manometry is advised when there is suspicion of an esophageal motility disorder. This can include conditions such as achalasia, esophageal spasms, or other conditions that affect the normal contractions of the esophageal muscles. Symptoms that may prompt a doctor to recommend esophageal manometry include difficulty swallowing, chest pain, regurgitation, or heartburn that is not responding to standard treatments. It may also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments for esophageal motility disorders.
The patient will be given specific instructions on preparing for esophageal manometry, which may include fasting for a certain period before the procedure and stopping certain medications. It is essential to follow these instructions carefully to ensure the procedure goes smoothly.
Esophageal manometry is generally a safe procedure, but there are some risks, including nosebleeds, discomfort, or irritation in the throat or nasal passages. Rarely, there may be a perforation or injury to the esophagus.
Esophageal manometry is performed by passing a thin, flexible tube through the nose and into the esophagus. The tube contains pressure sensors that measure the muscle contractions and relaxation in the esophagus.
Esophageal manometry is advised when there is suspicion of an esophageal motility disorder. This can include conditions such as achalasia, esophageal spasms, or other conditions that affect the normal contractions of the esophageal muscles. Symptoms that may prompt a doctor to recommend esophageal manometry include difficulty swallowing, chest pain, regurgitation, or heartburn that is not responding to standard treatments. It may also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments for esophageal motility disorders.
The patient will be given specific instructions on preparing for esophageal manometry, which may include fasting for a certain period before the procedure and stopping certain medications. It is essential to follow these instructions carefully to ensure the procedure goes smoothly.
Esophageal manometry is generally a safe procedure, but there are some risks, including nosebleeds, discomfort, or irritation in the throat or nasal passages. Rarely, there may be a perforation or injury to the esophagus.

PROCEDURES WE CONDUCT
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Don’t wait!!
Get consulted with our GI specialist today
Book your appointment effortlessly.
ANTRANG KNOWLEDGE RESOURCE
ANTRANG KNOWLEDGE RESOURCE
get in touch
We are just a phone call away when you need us!