DIFFICULTY IN SWALLOWING
Dysphagia can occur at any age, and it may be temporary or chronic. It can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, and it may lead to malnutrition, dehydration, and other complications.
DIFFICULTY IN SWALLOWING

Dysphagia can occur at any age, and it may be temporary or chronic. It can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, and it may lead to malnutrition, dehydration, and other complications.
OVERVIEW
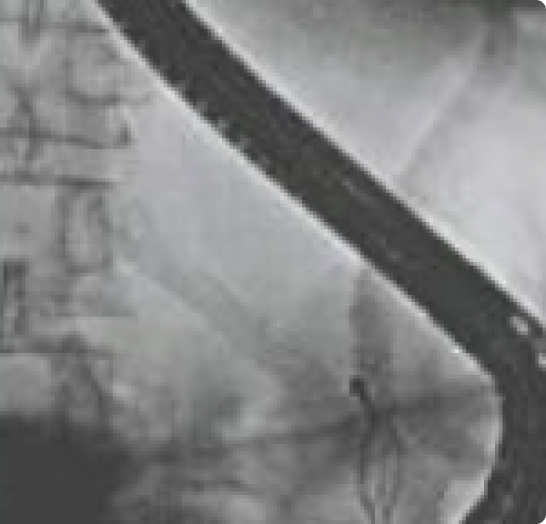
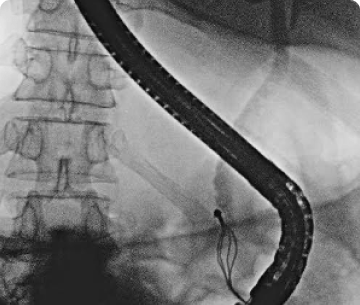
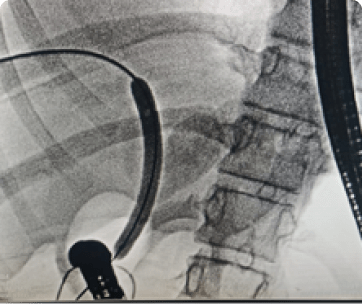
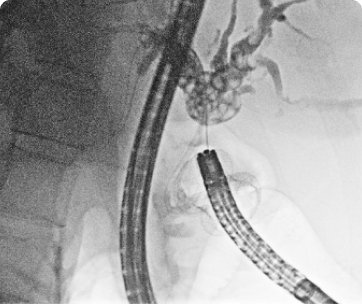
Difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia, is a condition in which there is a sensation of food or liquid getting stuck in the throat or chest while eating or drinking. Dysphagia can occur at any age, and it may be temporary or chronic. It can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, and it may lead to malnutrition, dehydration, and other complications.
Difficulty swallowing can be caused by a variety of conditions, including neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease or stroke, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), esophageal strictures or narrowing, tumors, infections, or other structural abnormalities of the esophagus.
Diagnosis of dysphagia typically begins with a physical examination and a thorough medical history. Depending on the suspected cause, additional diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies, endoscopy, or swallow studies, may be ordered to evaluate the esophagus and identify any underlying structural abnormalities or neurological conditions.
Treatment for difficulty swallowing depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes or swallowing exercises, may be recommended. Medications may be prescribed to manage underlying conditions, such as GERD or neurological disorders. In more serious cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to address structural abnormalities or remove tumors. It is important to work with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the underlying cause of the dysphagia.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent difficulty swallowing or if you have difficulty breathing or coughing while eating or drinking. Other symptoms that may indicate a more serious underlying condition include unexplained weight loss, chest pain, or vomiting.
Difficulty swallowing can be caused by a variety of conditions, including neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease or stroke, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), esophageal strictures or narrowing, tumors, infections, or other structural abnormalities of the esophagus.
Diagnosis of dysphagia typically begins with a physical examination and a thorough medical history. Depending on the suspected cause, additional diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies, endoscopy, or swallow studies, may be ordered to evaluate the esophagus and identify any underlying structural abnormalities or neurological conditions.
Treatment for difficulty swallowing depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes or swallowing exercises, may be recommended. Medications may be prescribed to manage underlying conditions, such as GERD or neurological disorders. In more serious cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to address structural abnormalities or remove tumors. It is important to work with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the underlying cause of the dysphagia.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent difficulty swallowing or if you have difficulty breathing or coughing while eating or drinking. Other symptoms that may indicate a more serious underlying condition include unexplained weight loss, chest pain, or vomiting.
Don’t wait!!
Get consulted with our GI specialist today
Book your appointment effortlessly.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS

MEET OUR DOCTORS
Our team comprises of well experienced and skilled medical professionals from all the allied medical specialties helped by young enthusiastic doctors.
MEET OUR DOCTORS
Our team comprises of well experienced and skilled medical professionals from all the allied medical specialties helped by young enthusiastic doctors.